 |
|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология |
Designing a new treatment strategy
We estimated the years of potential life lost—YPLL[21] from the number of cardiovascular deaths that would occur if no treatments were administered among the individuals potentially eligible and the 10-year mean life expectancy (Eq 2).
Eq 2 to calculate years of potential life lost due to premature death of cardiovascular origin. CVD: fatal cardiovascular disease; LE: mean life expectancy estimated from French official statistics reported in 2010[22]; i: the individuals in the category. We defined the proportional benefit as the ratio of the potential gain in life years under treatment over the expected years of life lost due to premature death of cardiovascular origin (Eq 3).
This proportional benefit estimated at the population level served as the reference for the equitable strategy. We computed the proportional benefit coefficient from the 2007 ESH/ESC guidelines implementation in the individuals potentially eligible of all ages and both genders, using the Eq 4: Дата добавления: 2015-11-26 | Просмотры: 452 | Нарушение авторских прав |
 (2)
(2)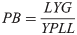 (3)
(3) (4)
(4)