|
|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология |
Vocabulary. 1) Match the words to their definitions
1) Match the words to their definitions. Say what types of caries do you know.
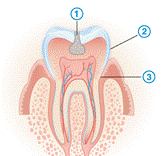
2) Label the picture
Дата добавления: 2015-02-05 | Просмотры: 868 | Нарушение авторских прав |