|
|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология |
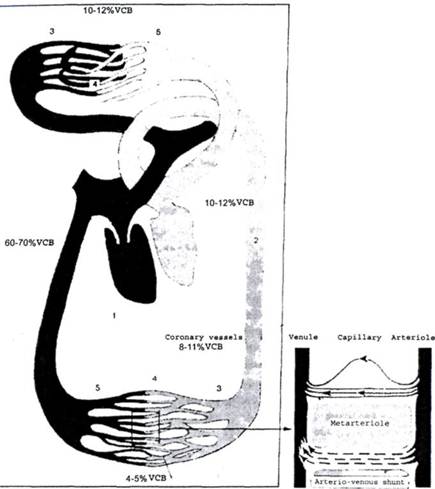
ACUTE CARDIOVASCULAR FAILURESystem of blood circulation consists of two sections (Fig. 29). System of macrocirculation: heart, buffer-vessels (aorta, pulmonary artery, arteries of systemic circuit) fulfiling transport function between the heart and system of microcirculation; capacity-vessels (veins), as well as carrying out transport function of blood return to the heart. They are more active and able to increase their volume 10 times and, thus, participate actively in VCB regulation. System of microcirculation, in its turn, consists of three sections: — vessels of distribution of cardiac output and resistance — arterioles and venules. They regulate a blood flow through capillaries since they are the main means of distribution of cardiac output to the organs and tissues; — vessels of exchange — capillaries through the walls of which the exchange of substances occurs between blood and tissues; — shunt-vessels — arteriovenous (A-V) anastomoses, direct com Vessels of blood circulation system by their resistance to the blood flow and perfusion pressure are subdivided into: — vessels with high pressure; — vessels with low pressure. Arteries of systemic circuit are referred to the system of high pressure. This system is characterized by small capacity (15-20% of VCB) and high pressure to strain. System with low pressure is presented by venous system of pulmonary and systemic circuits; it is characterized by great capacity (75-80% of VCB) and low resistance to strain. In its turn, the system with low pressure is subdivided into two sections: — with high motor activity — peripheral veins; — with low motor activity — caval and jugular veins. Hence, peripheral venous pressure is defined by tone of veins, and CVP — by their filling. The vessels are filled with a definite volume of blood. A notion exists that a total blood volume (TBV) makes up 7% of body weight. This is the total volume of blood being in the hemodynamic state. A volume of circulating blood (VCB) — it is the volume of blood that is in active circulation it is always lesser than TBV (5% of body weight). VCB in males is equal to 70 ml/kg, in females — 65 ml/kg.
Fig. 29. Functional sections of cardiovascular system: Дата добавления: 2015-02-05 | Просмотры: 1201 | Нарушение авторских прав |