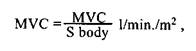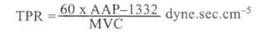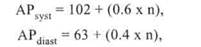|
|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология |
Acute disturbances of cardiovascular systemCardiac activity is conditioned by its main functions: automatism, excitability, conduction and contractility. These functions are interrelated, regulated by CNS and dependent on humoral influences. Myocardium — the basic mass of the heart, consists of particular cross-striated muscles and makes up 1/175 - 1/200 part of the human body mass. The thickness of the right atrium is 2-3 mm, the right ventricle — 5-6 mm, the left ventricle — 12 mm. The capacity of the right atrium of the adult man is 100-105 ml, the left ventricle — 220 ml. A blood supply of the heart is insured with coronary vessels. The state of coronary blood flow depends on the average arterial pressure in the aorta:
where AAP — an average arterial pressure, MSP — maximal (systolic) pressure, DP — diastolic pressure. The anatomical structure of coronary arteries has its peculiarities. At the place of the coronary artery branching there is a fold of aortic intima that is displaced when the blood is ejected from the left ventricle, closing the entrance to the lumen of coronary vessels, and during the diastole — it returns to its initial position, opening the entrance to the lumen of vessels. At this moment blood comes from the aorta into coronary vessels. Two processes take place in the heart continuously: conduction of impulse and transformation of chemical energy into mechanical one. Conduction system of the heart consists of: — Keith and Flack node. It is an automatic center of the first order. Under physiologic conditions it is a cardiac pacemaker with a frequency of 60-80 impulses per minute. It is located between atria; — atrioventricular Ashoff-Tawara node. It is the center of automatism of the second order with a frequency of impulses 40-60 per min.; — — Purkinje's fibers and other (accessory). Sinoatrial node sets the rhythm of operation for the whole myocardium. In the norm HR is equal to 60-90 beats per min. In injuries of sinoatrial node impulses arise in the underlying nodes where the frequency of impulses is lesser. Cardiac innervation is carried out with parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. N. vagus dexter approaches a sinoatrial node and n. vagus sinister approaches Ashoff-Tawara node. Thus, a vagal influence terminates in the region of atrioventricular node and the ventricles are not protected from cholinergic effects. Sympathetic innervation is ensured with nodes located in the upper thoracic and cervical parts of the spinal cord. Depot of acetylcholine (ACCh) in the heart is in the ventricles. SVH — a stroke volume of the heart is equal to 60-70 ml. Minute volume of circulation (MVC) = SVH x HR = 4.3-5.5 1/min. HR depends on many factors. Anesthesia may sharply change HR by influencing the activity of sympathoadrenal system.
Proceeding on this we draw a conclusion that MVC is the basic index of blood circulation system. There is such a notion as a cardiac index (CI).
where S — a body surface in m2. If CI is < 2.5 it is a hypodynamic state of blood circulation, CI = 3.0-3.9 — normodynamia, CI > 4.2 — hyperdynamia. Transitional states of blood circulation are also distinguished: relative hypodynamia — CI = 2.5-2.9, relative normodynamia, conventional hyperdynamia and relative hyperdynamia. A very important for the work of the heart is TPR index — total peripheral resistance.
Peripheral resistance influences a cardiac output. Arterial pressure is defined by the amount of blood pumped by the heart into the arterial system per time unit and resistance of vessels to the blood flow. Arterial pressure (AP) does not reflect all changes of hemodynamics in the organism and depends on VCB, MVC and TPR. In the norm AP can be calculated by the formulae:
where n — age in years. CVP — central venous pressure is the quantity representing a filling of caval veins with blood. In the norm CVP is equal to 60-120 mm water column. It is measured by method of tonometry in the right atrium or vena cava superior. A low CVP is the evidence of discrepancy of the vascular bed capacity and VCB. This is an indirect sign of hypovolemia. MVC, here, is always decreased. CVP > 120mm water column is usually the result of hypervolemia, but it may be high in myocardial weakness as well. If CVP increases and AP decreases — then it is a question of cardiac weakness, low AP and CVP is the evidence of hypovolemia, high AP and CVP — are the signs of hypervolemia. Total blood volume (TBV) and volume of circulating blood (VCB) are different notions. TBV is always greater than VCB (7% of body weight and 5%). The brain makes up 2% of body mass, but it receives 15% MCV Cerebral blood flow makes up 50-60 ml per 100 g of tissue per minute (35% of total oxygen consumption). Дата добавления: 2015-02-05 | Просмотры: 1102 | Нарушение авторских прав |

 His' bundle is the center of automatism of the third order with a frequency of impulses 20-30 per minute, it consists of two peduncles (right and left);
His' bundle is the center of automatism of the third order with a frequency of impulses 20-30 per minute, it consists of two peduncles (right and left);