 |
|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология |
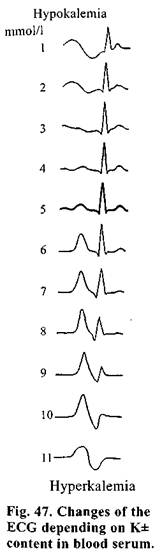
CLINICAL PICTURE OF ACUTE RENAL FAILUREIt is accepted to divide a course of ARF into 4 stages. Initial stage — a clinical picture depends on the nature of agent caused ARF. A severity of developed ARF will depend on the nature of aggressive factor, pathogenetic mechanism of action and duration of effect. One of the most important symptoms, at this period, is not as much an oliguria as the signs of the disturbance of concentration ability of tubular epithelium. A specific gravity of the urine, as a rule, is 1005-1006. A urea content in blood serum, somewhat, elevates (to 17-20 mmol/1). Events of uremic intoxication and dyselectrolytemia are not observed a clinical picture depends, entirely, on the basic disease. Oligoanuric stage is the main stage of the disease. The gravest changes take place in the organism at this period. This stage accounts for the greatest number of fatal outcomes. A predominant clinical sign is oliguria-anuria. A diurnal urine excretion makes up from 10-15 to 200-300 ml in invariable hyposthenuria (a specific gravity 1002-1008). Anuric stage is not obliged to advance right after the initial stage, but may manifest itself in 4-5 days. The urine, at this stage, is cloudy, dark, dark-brown or bloody. A protein content is sharply increased. Numerous formed elements of blood are found in the sediment. Rather specific are clods of hemin casts (in hemotransfusion complications, intravascular hemolysis of other origin), crystalline myoglobin (crush syndrome), crystals of sulfanilamides (in their toxic effect). Contents of urea and creatinine are elevated in the urine (30-40 mmol/1 or 300-400 mmol/1, respectively). In blood there is often significant leukocytosis (up to 30-60 g/1), a shift of differential blood count to the left, anemia, elevation of ESR. Depending on the cause of ARF patients' condition may be both satisfactory and extremely grave. Clinically it may be manifested by both dryness (a sign of hypohydration) and increased moisture (loss of electrolytes and hypotonia of plasma) of cutaneous coverings. Anorexia is always observed, nausea and vomiting aggravate even greater, a disgust to food. Dryness in the mouth, cracks of mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue, stomatitis and, sometimes, persistent hiccough appear. In the first days constipation may be observed turning later into a persistent diarrhea. Excretion of urea and other products of nitrogen metabolism by mucous membrane of GIT leads to gastroenterocolitis.Peritonism may also be observed (abdominal syndrome simulating peritonitis), as a result of growing acidosis — dyspnea, and in overdosage of introduced liquid — a moist lung ("fluid lung"): in auscultation — no rales, on X-ray film — a shadow around the root of the lung in the form of "butterfly". An increase of potassium ions concentration and intoxication of the myocardium are manifested by characteristic changes of the ECG (Fig. 47). Pi lse is accelerated, arterial pressure — reduced, diastolic pressure may not be determined, bu: in some patients a hypertension is noted. Venous pressure increases to 200-250 mm water column and develops a pulmonary hypertension. Sometimes, pains in the renal region are observed (in the beginning they are caused by vascular spasm, then by interstitial edema; quite often they are conditioned by development of hematomas in pararenal fat as a result of traumas or as an error of paranephric block). A state of consciousness depends on the level of intoxication and ranges from clear to comatose. Duration of this stage is, on the average, 7-18 days. Stage of recovery of diuresis, usually, runs as Later a concentration ability of the kidneys is restored, azotemia decreases to subnormal level, water-electrolyte balance is being recovered. Appetite gets better, changes in the function of cardiovascular system and CNS disappear. Anemia persists for a long time. Duration of this stage is to 2 months. Stage of recovery is the most prolonged, in the majority of patients from 6 months to 2 years. Quite often the signs of insufficiency of individual functions are preserved. Дата добавления: 2015-02-05 | Просмотры: 1004 | Нарушение авторских прав |
 two steps. In the first 3-4 days it is manifested by insignificant diuresis (400-600 ml). Hereafter, the amount of urine progressively increases and leads to polyuria, diuresis achieves 6-7 1/day. The urine has a low specific gravity since a concentration ability of the kidneys remains low. The electrolyte disorders are maintained and even aggravated (hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia). Quite often, at this phase, in spite of polyuria, the obvious signs of uremic intoxication are manifested and being kept.
two steps. In the first 3-4 days it is manifested by insignificant diuresis (400-600 ml). Hereafter, the amount of urine progressively increases and leads to polyuria, diuresis achieves 6-7 1/day. The urine has a low specific gravity since a concentration ability of the kidneys remains low. The electrolyte disorders are maintained and even aggravated (hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia). Quite often, at this phase, in spite of polyuria, the obvious signs of uremic intoxication are manifested and being kept.