|
|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология |
ECTOPIC COMPLEXES AND RHYTHMS
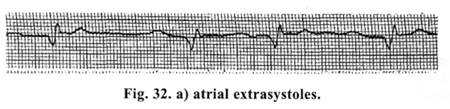
This is the main bulk of arrhythmias that arise as a result of increa;ed excitability of any area of heart conduction system. The latter is associated with increased ability of cells of conduction system to spontaneous depolarization. Extrasvstoles — are premature, out of order ectopic cardiac contractions (?). — Supraventricular extrasvstoles (atrial) (Fig. 32 a) do not cause
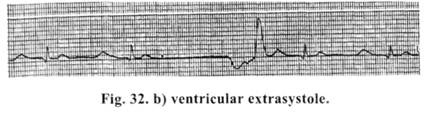
A sharply deformed P-wave is registered, prematurely appeared after T-wave. A compensatory pause is incomplete (less than 2 R-R), ventricular complex, on ECG, is not changed and is identical. Polytopic, group atrial extrasystoles are the precursors of ciliary arrhythmia. Here, premature contractions are felt even clinically. Treatment is carried out if there are more than 6 extrasystoles per min./3-blockers and calcium antagonists, in the form of tablets, are prescribed for treatment, in expressed hemodynamic disorders — injection forms of the same preparations. Ventricular extrasvstoles (Fig. 32 b) — are the predictors of very grave prognostic outcomes. They may be polytopic and group and are, usually, the predictors of ventricular fibrillation.
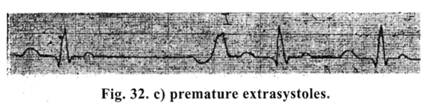
Absence of P wave is noted on ECG. A ventricular complex is sharply deformed and distorted. A complete compensatory pause (2 R-R) is registered. — Premature extrasvstoles (Fig. 32 c) arising just after T wave are the predictors of ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular and premature extrasystoles require a prescription of lidocaine in the dosage of 0.5-1.0 mg/kg.
— Parasystole (Fig. 33) — is an arrhythmia conditioned by availability of two or more pacemakers one of which is protected from the impulses of another.
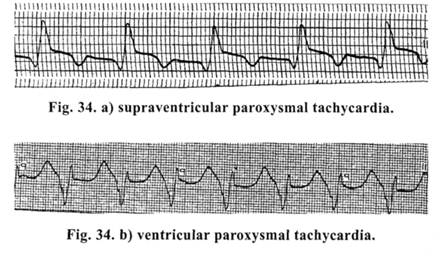
Paroxysmal tachycardia. The difference between sinus and paroxysmal tachycardia is in the rate of cardiac contractions and clinical manifestations. Supraventricular and ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia and paroxysms of ciliary arrhythmia are distinguished. On ECG in supraventricular and paroxysmal tachycardia (Fig. 34 a) QRS complex is of normal configuration, only in a very frequent rhythm (150-250 per min). In ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia (Fig, b) frequent, greatly altered QRS complexes are registered and P waves are absent. This kind of paroxysmal tachycardia is dangerous by a possibility of rapid transition into fibrillation.
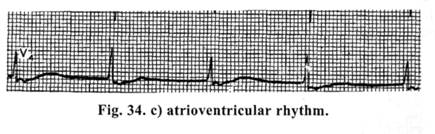
Atrioventricular rhythm. (Fig. 34 c). It arises from the lower part of atrioventricular node and the upper part of trunk of His' bundle. Here, on the ECG P-wave is absent before QRS complex. QRS complex is not changed or widened and has a usual form.
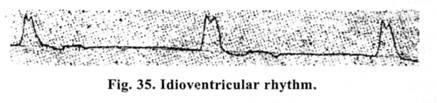
Idioventricular rhythm. (Fig. 35). It arises in cases when Purkinje's fibers take upon themselves the function of the pacemaker. The rhythm is rare (18-20 per min) and aberrant. A picture of complete A-V block with sharply deformed widened QRS complexes is noted on ECG. It produces an acute disorder of hemodynamics and requires urgent therapy, since the picture of electromechanical dissociation or "ineffective heart" develops very fast, that needs carrying out cardio-pulmo-cerebral resuscitation.
Idioventricular rhvthm. (Fig. 35). It arises in cases when Purkinje's fibers ta k e upon themselves function of the the pacemaker. The rhythm is rare (18-20 per min) and aberrant. A picture of complete A-V block with sharply deformed widened QRS complexes is noted on ECG. It produces an acute disorder of hemodynamics and requires urgent therapy, since the picture of electromechanical dissociation or "ineffective heart" develops very fast, that needs carrying out cardio-pulmo-cerebral resuscitation.
Дата добавления: 2015-02-05 | Просмотры: 928 | Нарушение авторских прав |