|
АкушерствоАнатомияАнестезиологияВакцинопрофилактикаВалеологияВетеринарияГигиенаЗаболеванияИммунологияКардиологияНеврологияНефрологияОнкологияОториноларингологияОфтальмологияПаразитологияПедиатрияПервая помощьПсихиатрияПульмонологияРеанимацияРевматологияСтоматологияТерапияТоксикологияТравматологияУрологияФармакологияФармацевтикаФизиотерапияФтизиатрияХирургияЭндокринологияЭпидемиология
|
SPECIFIC (ANTIDOTE) THERAPY
It is prescribed in relatively small number of toxic substances. It requires absolutely exact diagnosis and is effective only at the early toxicogenic stage. The main antidote therapy is given in Table 28.
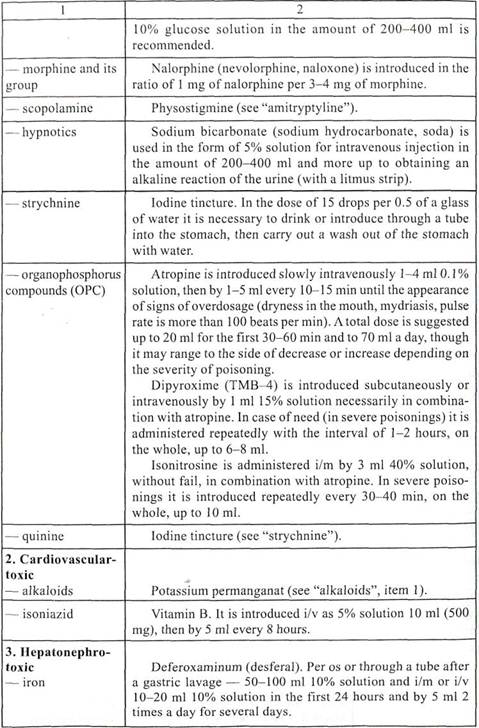
Table 28 Specific (antidote) therapy
| Poisons
| Antidotes
| |
|
| | 1. Neurotoxic
— alkaloids
| Potassium permanganat is used in the form of aqueous solution 1:10000 for a gastric lavage, but after this the stomach is to be washed out with pure water until all residues are removed. Its solution is prepared by dissolving 1 g (on the point of a knife) inlOO ml of water and brought to 10 1. While preparing this solution one should see to a thoroughness of dissolution to avoid a cauterizing effect of crystals that are not yet dissolved upon mucous membranes.
Milk. It is used in dilution with water 1:1 for a gastric lavage or introduced into a tube in the amount of 1-1.5 glass of milk and then a gastric lavage is carried out.
A white of an egg. No less than 10 eggs are given or introduced through a tube into the stomach, then the stomach is to be washed out without fail.
| | — amitryptyline
| Physostigmine (eserine, proserine) is introduced slowly intravenously 2 ml 0.1% solution. In case of need it is introduced repeatedly twice in the same dose with a 20-min interval. It is contraindicated in bronchial asthma, ischemic heart disease, ileus, urinary tract obstruction.
| | — atropine
| Physostigmine (see "amitryptyline").
| | — bromides
| Sodium chloride (table salt). 1 teaspoon of sodium chloride per 1 1 of water for a gastric lavage, then by 1 g dissolved in water per os every hour up to a disappearance of signs of poisoning (approximately by 100 ml of the above given solution).
| | — petroleum distillates
| Paraffin oil per os by 200-300 ml prior and 100-200 ml after a gastric lavage.
| | — methyl alcohol
| Ethyl alcohol. It is introduced by 50-100 ml 50% solution every 4 hours for the course of 1-3 days or intravenously in the form of 5% solution per 4% soda solution or physiologic sodium chloride solution by 100-150 ml an hour up to 2-3 1 a day. Simultaneously with the intake or infusion of ethyl alcohol an administration (perorally or intravenously) of 5-
|
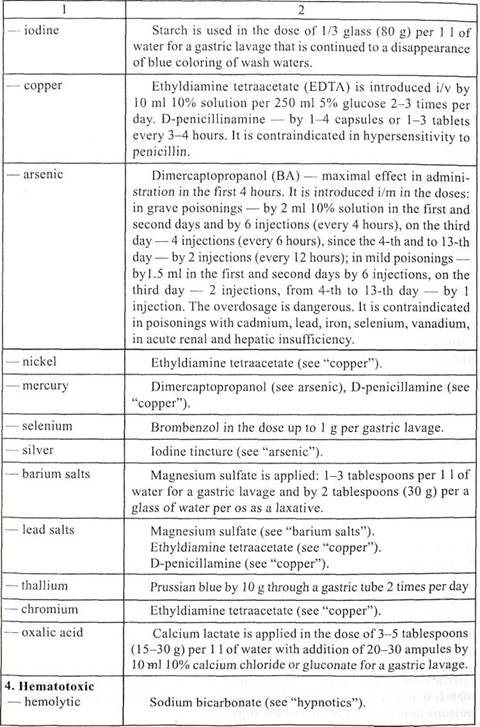
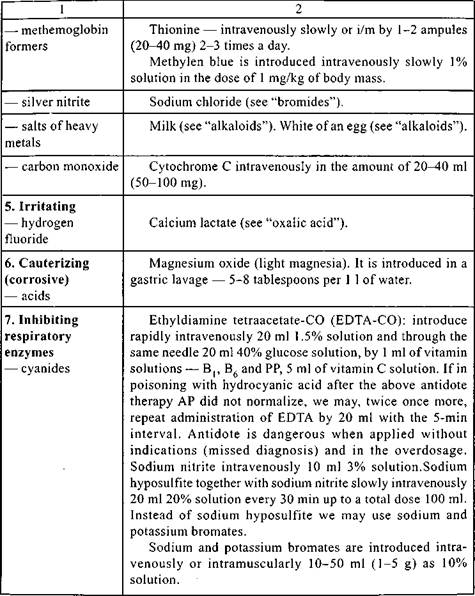
Table 28 (continued)
Table 28 (continued)
Table 28 (continued)
A description of the most often occurring kinds of poisonings is given below.
Дата добавления: 2015-02-05 | Просмотры: 975 | Нарушение авторских прав
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 | 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 | 110 | 111 | 112 | 113 | 114 | 115 | 116 | 117 | 118 | 119 | 120 | 121 | 122 | 123 | 124 | 125 | 126 | 127 | 128 | 129 | 130 | 131 |
|